Laser spectroscopy of van der Waals molecules produced in free-jet supersonic beams
 produced in supersonic beams
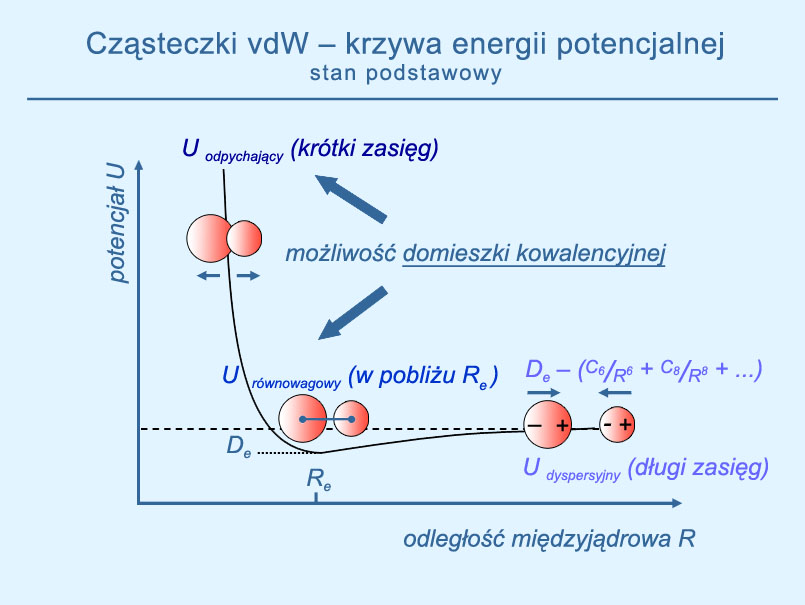
produced in supersonic beams 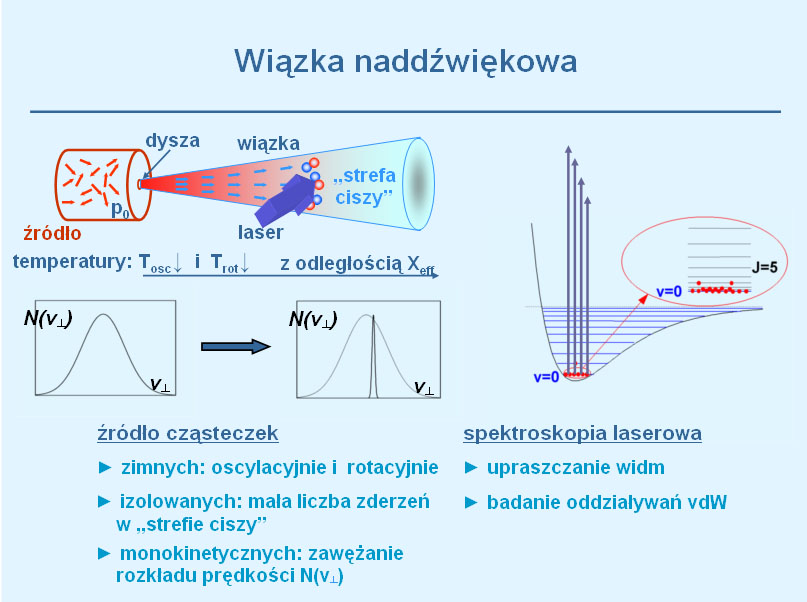 is a source of information on the ground- and excited-state interatomic potentials. The goal of the research is to provide a comprehensive characterisation of the MeRG and Me2 diatoms, where Me and RG are 12-group (Zn, Cd, Hg) and rare gas atoms, respectively [Science Direct].
is a source of information on the ground- and excited-state interatomic potentials. The goal of the research is to provide a comprehensive characterisation of the MeRG and Me2 diatoms, where Me and RG are 12-group (Zn, Cd, Hg) and rare gas atoms, respectively [Science Direct].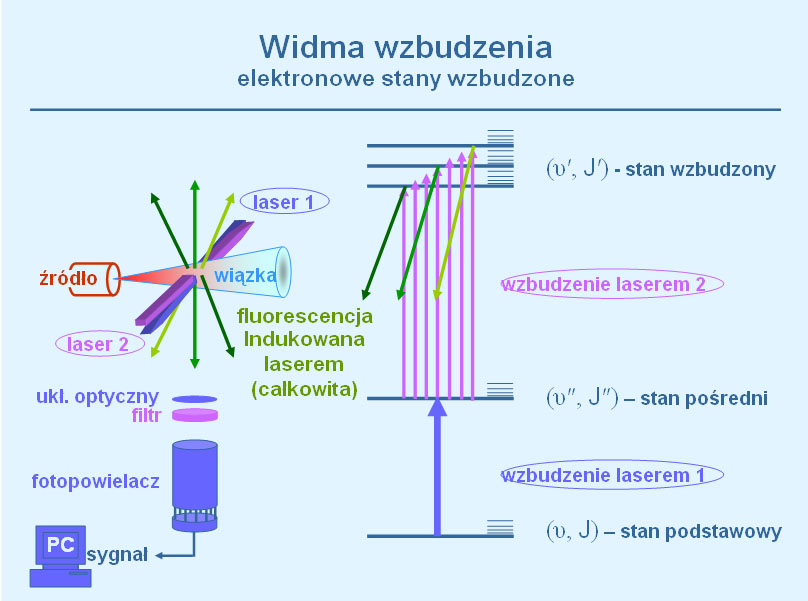 excitation spectra and fluorescence spectra
excitation spectra and fluorescence spectra  of the Me2 and MeRG molecules using methods of laser spectroscopy. Rotational strctures in Hg2 are studied within a cooperation with group of E. Fry of Texas A&M University in College Station, TX. Calculation of molecular potentials are performed in cooperation with M. Krosnicki of University of Gdansk and C. Western of University of Bristol. Cooperation with group of University of Windsor brings still new results on spectroscopy of extremely weak CdHe complex.
of the Me2 and MeRG molecules using methods of laser spectroscopy. Rotational strctures in Hg2 are studied within a cooperation with group of E. Fry of Texas A&M University in College Station, TX. Calculation of molecular potentials are performed in cooperation with M. Krosnicki of University of Gdansk and C. Western of University of Bristol. Cooperation with group of University of Windsor brings still new results on spectroscopy of extremely weak CdHe complex.
The research was supported by State Committee for Scientific Research within two research projects:
1. "Ro-vibrational structures of van der Waals molecules studied using method of supersonic molecular beam crossed with laser beam", project KBN 2 P03B 107 10 (description in Polish).
2. "Properties of van der Waals bonding in diatomic molecules in different regions of internuclear distances", project KBN 5 P03B 037 20 (description in Polish).
Presently the research is supported, among others, by Ministry of Science and Higher Education within projects:
"Cold molecules in supersonic beams and properties of interatomic bond - do we have to change our perceptio of van der Waals molecules?", project N202 067 32/1399 (description in Polish).
"Studies of rotations in van der Waals dimers - complexity of molecular potentials in sub-nano scale and their interdisciplinarity", project N N202 2137 33 (description in Polish).
The most important results:
(references are located in Publications)
1. Characterization of weakly - bound CdHe [Journal of Chemical Physics, Science Direct] and ZnNe [Physical Review Archive]and characterization of their ground and lower excited electronic states.
2. Studies of the E31(3Σ+)Rydberg states in CdNe [Science Direct], CdAr [Science Direct] and CdKr [Physical Review Archive].
3. Observation of the B31←X10+ [Acta Physica Polonica B], 31u←X10+g [Science Direct] and E31u←X10+g [Canadian Journal of Physics] transitions in the excitation spectra of the CdXe, Cd2 i Hg2; respectively: characterization of the B31, 31u i E31u excited states.
4. Investigation of the D11v′=10→X10+ [Science Direct], B31v′=0-3 →X10+ [Science Direct], A30+v′=8→X10+ [Science Direct], G10+u , v′=39→X10+g [Science Direct] and 10+u , v′=38,39 →X10+g[Physical Review Archive] , [pdf] transitions in the fluorescence spectra of the ZnAr, HgAr, HgKr, Hg2 and Cd2 respectively: characterization of the repulsive parts of the ground state.
5. Direct observation of the B31-state dissociation limits in the HgAr [Journal of Chemical Physics] and CdAr [Science Direct]: reliable description of the long-range behaviour of the B31-state potentials.
6. Direct characterisation of the ground-state potentials of the ZnNe [Physical Review Archive], ZnAr [Science Direct], CdHe [Journal of Chemical Physics, Science Direct], CdAr [Science Direct], HgNe [Science Direct], HgAr [Science Direct] and Cd2 [Science Direct] using observed “hot” bands: superseding previous, indirect ground-state characteristics, sometimes erroneous or inaccurate.
7. For the CdNe [Spinger Link] and CdKr [AIP Proceedings, Science Direct] molecules an interpretation of the B31←X10+ transitions in their excitation spectra is corrected with respect to the previous analyses: enhanced representations for the B1-state potentials.
8. A special emphasis is put on characterisation of ground-state repulsive branches of interatomic potentials from the observed fluorescence spectra. Consequently, the ground-state short-range repulsive walls of the ZnAr [Science Direct] and HgKr [Science Direct]. molecules are directly determined. The determination is more accurate when two “channels” of the fluorescence terminating on the same part of the ground-state repulsive branch are used for the analysis: CdNe [Spinger Link], CdAr [Science Direct], CdKr [Science Direct] and HgAr [Science Direct] fluorescence spectra.
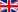
9. An unusually soft repulsive wall of the ground-state Mg2 and Cd2 are determined, supporting a hypothesis of short-range induction effects playing a significant role in the stabilization of Hg2 [Science Direct] and Cd2 [Physical Review Archive]. A theoretical prediction of covalent bonding contributions to the Me2 ground-state interaction potential has been partly confirmed in experimental observations.
10. Analysis and simulation of transitions in rotational branches of homonuclear isotopomers of the Cd2 molecule [Science Direct].